Hardcover, 336 pages
English language
Published Nov. 7, 2018
Hardcover, 336 pages
English language
Published Nov. 7, 2018
Does Silicon Valley deserve the credit it gets for digital creativity and social media? Joy Lisi Rankin questions this triumphalism by revisiting a pre-PC world where schools were not the last stop for mature consumer technologies but flourishing sites of innovative collaboration.
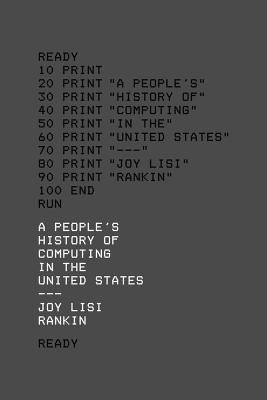
A People's History of Computing in the United States reveals a forgotten time when students taught computers, rather than the other way around, and visionaries dreamed of networked access for all. The invention of the personal computer undoubtedly liberated users from corporate mainframes and brought computing into homes. But throughout the 1960s and 1970s a diverse group of teachers and students working together on academic computing systems conducted many of the activities we now recognize as personal and social computing. Their networks were centered in New Hampshire, Minnesota, and Illinois, but they connected far-flung users.
Rankin draws on detailed records to explore how users exchanged messages, programmed music …
Does Silicon Valley deserve the credit it gets for digital creativity and social media? Joy Lisi Rankin questions this triumphalism by revisiting a pre-PC world where schools were not the last stop for mature consumer technologies but flourishing sites of innovative collaboration.
A People's History of Computing in the United States reveals a forgotten time when students taught computers, rather than the other way around, and visionaries dreamed of networked access for all. The invention of the personal computer undoubtedly liberated users from corporate mainframes and brought computing into homes. But throughout the 1960s and 1970s a diverse group of teachers and students working together on academic computing systems conducted many of the activities we now recognize as personal and social computing. Their networks were centered in New Hampshire, Minnesota, and Illinois, but they connected far-flung users.
Rankin draws on detailed records to explore how users exchanged messages, programmed music and poems, fostered communities, and developed computer games, including The Oregon Trail. No less than the male inventors, garage hobbyists, and eccentric billionaires of Palo Alto, these unsung pioneers helped shape our digital world. By imagining computing as an interactive commons, the early denizens of the digital realm seeded today's debate about whether the internet should be a public utility and laid the groundwork for national and international debates over net neutrality. Rankin offers a radical precedent for a more democratic digital culture, and new models for the next generation of activists, educators, coders, and makers.--